Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Want to be energy independent and cut down on grid use? Designing an off-grid solar system is a smart move. This guide will show you how to create a system that fits your power needs. It ensures a steady and green energy supply for your home or land.
Whether you’re new to solar or have DIY skills, this guide has what you need. You’ll learn how to size solar panels and batteries and pick the right inverter. I’ll cover all key parts and design tips for your energy freedom.

Creating an off-grid solar system needs a deep understanding of its parts and what to consider. These systems work on their own, perfect for places far from the main power grid. They are great for remote homes, cabins, RVs, or areas where power lines don’t reach.
To design an off-grid solar system, start by figuring out how much power you need. Then, pick the right parts and size them right. This guide will walk you through the basics of making an off grid solar system or designing off grid solar power system.
Knowing these parts and following a plan can help you make a reliable off-grid solar system. Success comes from good planning, picking the right parts, and sizing them correctly. This way, you get a steady and independent power source.

“Solar energy has the potential to handle the entire world’s energy consumption for a full year with just an hour and a half of sunlight.”
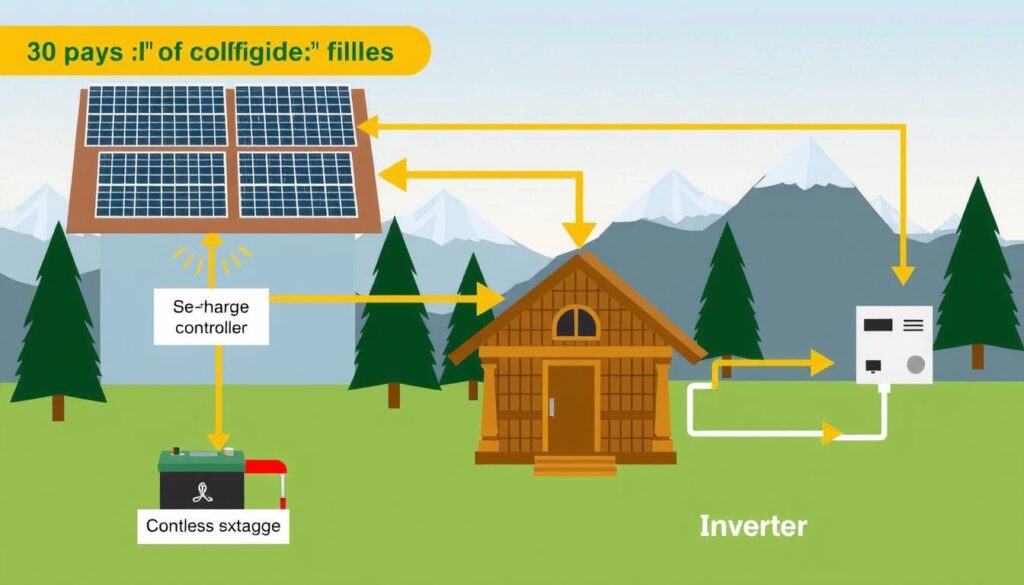
To make an off-grid solar system work well, you need to know the main parts. These parts are solar panels, a charge controller, a battery bank, and an inverter. Let’s look at what each does.
Solar panels are the core of an off-grid solar system. They turn sunlight into electricity. The type of panel you choose affects how well the system works.
Monocrystalline panels are more efficient but cost more. Polycrystalline panels are cheaper but less efficient.
The charge controller manages the electricity flow from panels to batteries. It keeps batteries from getting too full or too empty. This helps the system last longer and work better.
There are three types of charge controllers: ON/OFF, MPPT, and PWM. MPPT controllers are the best but also the priciest. PWM controllers are a good middle ground.
The battery bank holds electricity for when it’s dark or not sunny. Deep-cycle batteries are best for this because they can handle being used a lot. The size of the battery bank depends on how much power you need and how often you want to use it.
The inverter changes DC electricity from batteries to AC for appliances. There are three types: Square Wave, Modified Sine Wave, and Pure Sine Wave. Pure Sine Wave inverters are the best because they work with most devices.
Knowing how these parts work is key to setting up a good off-grid solar system. By picking the right parts and putting them together, you can have a reliable, green power source for your home or off-grid place.
Creating an off-grid solar system needs a clear plan. This ensures your energy needs are met well. Let’s look at the main steps to make a system that fits your needs.
Start by figuring out how much energy you use each day. Use a load table or an off-grid load calculator. This helps size your solar system’s parts.
Then, size your battery bank for enough storage. This lets your system work when it’s dark or sunny. Think about your daily use, battery type, and how long you want it to last.
After knowing your energy needs and battery size, figure out your solar array size. Calculate the solar panel wattage needed to charge batteries and meet daily loads. The size depends on your energy needs and sunlight hours.
Picking the right inverter is key for powering your home. Choose one with the right power ratings for your needs. This ensures your appliances and devices work well.
Adding a backup source, like a diesel generator, is optional. It helps when sunlight is low. This ensures you always have enough power.
By following these steps, you can create an off-grid solar system that meets your energy needs. It will provide reliable power for your home or property.
Choosing the right off grid inverter is key to a good off-grid solar system. It must handle your system’s power needs and any sudden spikes from appliances. This is important for reliable power.
The off grid inverter should have a power rating a bit higher than your system’s max demand. This is to account for temperature changes and other factors. It makes sure the inverter can power your system without getting too hot.
Knowing your system’s maximum demand is crucial. It’s the highest load the off grid inverter will face. To find this, add up the power needs of all your electrical devices. This helps size your inverter correctly.
Also, think about the inverter’s surge or peak power. This is important for loads like pumps or compressors. Make sure the inverter’s specs match your system’s needs for efficient power.
By considering these points when selecting off grid inverters, you can size and design your system well. This ensures it meets your power needs effectively.
Designing an off-grid solar system is complex. It needs a deep understanding of your energy needs, site constraints, and system parts. Unlike grid-tied systems, off-grid ones must be fully self-sufficient. They must generate, store, and manage all the power for your daily needs. A thorough design ensures your system works well for a long time.
The design process has several key steps:
By using this detailed design method, you can make an off-grid solar system that meets your energy needs. It works well even when there’s no grid or you’re in a remote area. With good planning and the right gear, you can live off the grid with freedom and self-reliance.
“The key to a successful off-grid solar system is designing it with a thoughtful, comprehensive approach that considers all the unique requirements and constraints of your specific situation.”
If you know a bit about electrical work, setting up a small off-grid solar system can be fun. This guide will show you the key parts and tools you need for a DIY off-grid solar system.
To make your own off-grid solar system, you’ll need a few important things:
You’ll also need the right tools for the job, like:
While big or complex systems should be done by pros, a small one can be a great DIY project. With the right tools and some basic electrical knowledge, you can set up a diy off grid solar system installation. It will give you reliable, green energy for your home or off-grid life.
Getting your daily energy use right is key to a good off-grid solar system. You need to list out all your appliances, lights, and gadgets. Then, figure out how much power they need.
Think about the power each item uses, how long it’s on, and if it’s used at the same time. This helps you know how much energy you need every day. Knowing this is important for choosing the right size for your system, like batteries and solar panels.
| Load Category | Wattage | Usage Time (hrs/day) | Daily Energy (Wh) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lighting | 240 | 5 | 1,200 |
| Refrigerator | 300 | 12 | 3,600 |
| TV | 150 | 4 | 600 |
| Laptop | 60 | 8 | 480 |
| Total Daily Energy Consumption | 5,880 Wh | ||
The table shows how to figure out your daily energy use for an off-grid solar system. Just add up the power and time for each item. This tells you how much energy you need in watt-hours (Wh).
Things like changing seasons, growing your system, or adding electric cars can change your energy needs. A good plan helps make sure your system can handle your energy needs well and efficiently.
When setting up an off-grid solar system, the battery bank is key. It stores energy from the solar panels. Picking the right battery and the right size for your battery bank is vital for reliable power. Let’s look at what to consider when choosing batteries for your off-grid solar system.
Lead-acid and lithium-ion are the top battery types for off-grid solar systems. Lead-acid batteries are cheaper but need more upkeep. Lithium-ion batteries, on the other hand, are more efficient, last longer, and need less care. Industry data shows solar batteries cost between $10,000 and $20,000 installed, with lithium-ion being pricier. Yet, lithium-ion batteries can pay for themselves in just five years, making them a great choice for off-grid systems.
It’s important to understand the differences between lead-acid and lithium-ion batteries. Also, know what affects the size of your battery bank. Making the right choice ensures your off-grid system works efficiently and reliably for your needs.
First, figure out how much energy you need each day. Then, pick the right battery bank. Next, size the solar panels and charge controller correctly. The solar array must produce enough power for your daily needs and recharge the batteries. Consider peak sun hours, shading, orientation, and temperature when sizing.
To size the solar panels, calculate your daily energy needs. For example, if you use 1,800 watt-hours a day and get 5 peak sun hours, you need at least 360 watts of solar array capacity.
The charge controller manages power flow from panels to batteries. It prevents overcharging or over-discharging. Choose a charge controller that fits your solar array and battery system. For instance, a 1 kW solar array and 24V battery bank need a charge controller rated for at least 52.09 amps.
Getting the solar panels and charge controller right is key. It ensures your off-grid solar system works well and meets your power needs.
“Properly sizing the solar panels and charge controller is crucial for the reliability and efficiency of an off-grid solar system.”
The inverter is key in an off-grid solar system. It changes DC electricity from solar panels and batteries into AC power for home use. Picking the right inverter is crucial for good power conversion.
When choosing an inverter, consider these important factors:
You’ll also need to pick between pure sine wave and modified sine wave inverters. Pure sine wave inverters are best for off-grid systems. They run more appliances and electronics well. Modified sine wave inverters are cheaper but might not work with all devices, leading to heat, noise, and power issues.
By carefully picking the right inverter, you can ensure reliable power for your off-grid solar system.
| Inverter Type | Characteristics | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pure Sine Wave Inverter | Produces a pure sinusoidal waveform, similar to grid power | Can efficiently run all types of household appliances and electronics Produces clean, stable power Longer lifespan for connected devices | Generally more expensive than modified sine wave inverters |
| Modified Sine Wave Inverter | Produces a stepped waveform that approximates a sine wave | Less expensive than pure sine wave inverters | May not be compatible with all devices Can cause increased heat, noise, and power surges in some appliances Shorter lifespan for connected devices |
Choosing the right cable size and making a clear wiring diagram are key steps for an off-grid solar system. The cables must carry the expected current without losing too much voltage or getting too hot.
For solar installations, THW and THHN cables are common. They are rated for different temperatures. When picking cables, think about the voltage, current, and how much voltage drop is allowed.
In a 1kW PV system with four 250W panels, a 12 AWG PV wire works well for connections from panels to charge controller. For connections from charge controller to battery bank, a 10 AWG THHN or THWN-2 cable is best for a 24V system with 50 A current. For the battery to inverter connection in a 2200W, 24V system, a 4 AWG THHN cable is suitable.
| Cable Segment | Recommended Cable Size |
|---|---|
| Panels to Charge Controller | 12 AWG |
| Charge Controller to Battery Bank | 10 AWG THHN or THWN-2 |
| Battery Bank to Inverter | 4 AWG THHN |
| DC Loads (Lights, Fans) | 12 AWG THW |
| DC Loads (Pumps) | 10 AWG THW |
A detailed wiring diagram is also crucial. It should show how all parts of the system connect. This makes installation easier and ensures the system works right. Paying attention to these details helps avoid problems and keeps your system running smoothly.
Creating an off-grid solar system might seem hard, but it’s doable with the right steps. This guide helps you make a dependable power source for your home. You’ll learn how to figure out your energy needs and choose the right parts.
While big systems need a pro, a small off-grid solar setup can be a fun DIY project. With careful planning and execution, you can enjoy clean, green energy. This means you’re not tied to the utility grid anymore.
This article wraps up by stressing the need for a detailed design process. It shows how even small systems can be DIY projects. But, bigger ones might need a pro. The goal is to achieve energy freedom with your off-grid solar system.
An off-grid solar system has four key parts. These are solar panels, a charge controller, a battery bank, and an inverter.
To figure out your daily energy use, make a load table or use a load calculator. This helps you see how much power your appliances, lights, and devices need.
Choosing the right battery bank involves a few things. You should look at lead-acid versus lithium-ion batteries. Also, think about depth of discharge and temperature derating to find the right size.
To size your solar array, consider your daily loads and how much power you need. Think about peak sun hours, shading, and temperature. Your charge controller should match your solar array and battery system.
When picking an inverter, look at its continuous power rating and maximum demand. Also, check its surge or peak power output. This ensures it can handle all your devices.
If you know a bit about electrical work, you might install a small off-grid system. But, bigger or more complex systems should be done by licensed pros.
Correct cable sizing and a clear wiring diagram are key for your system’s safety and efficiency. The cables must handle the current loads without too much voltage drop or heat.